Android NDK AAC decoder ADTS alignment
After a long thought, I finally decided to switch my blog articles to english, and continue to give some rare and mostly unintresting info in free form. And today we will talk more about Android, NDK and some undocumentated video/audio functionality, maybe will discover some new knowlage about AAC and maybe it will help your own problem, like it was for me. In a focus of this acrticle is Android AAC decoder, and a little detail how the decoding in android working behind NDK documentation.
AMediaCodec using steps
First let take a very very surface look how to start decoding using NDK:
- Create AMediaCodec using codec name.
- Configure AMediaCodec via AMediaCodec_configure.
- Ctart decoding AMediaCodec_start.
- Give a buffer using AMediaCodec_getInputBuffer.
- Back buffer with AMediaCodec_queueInputBuffer.
- Repeat while you have an buffer ;).
Looks very simple, and work good as well. I can end this article in this place, but I don’t tell you nothing about buffer requirenments and other stuffs, and in NDK/SDK also all simple like that. So what going on behind this android decoding? What if you getting some error with your buffer, or you don’t have sound in some rare cases? How the Android decoder works like, let take a look at AAC audio decoder as example. Let’s begin from simple.
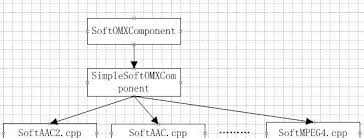
As you see on this bad jpeg picture :) Android have different implementation of AAC decoders as OMX components. But that’s not all, beside some software implemetation on some platforms existed hardware implementation, like on Broadcom chips. Keep at mind, and will transport to SoftAAC2 decoder. Let take a look deeper.